Water-soluble quenching medium (1)
001 still water medium
[Introduction] Static water can be tap water and distilled water. The advantages of the water medium are high heat of vaporization, high heat transfer coefficient, good chemical stability and low cost. It is easy to use, has a wide source and is not easy to deteriorate. It is a quenching medium with strong cooling capacity. The disadvantage of aqueous media is that the cooling rate changes significantly with changes in water temperature.
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] In the "nose" area of ​​the C curve (about 500 to 600 °C), the water is in the vapor film stage, and the cooling is not fast enough to form a "soft point"; in the martensite transformation temperature range (300 to 100) °C), in the boiling stage, the cooling is too fast, and the martensite transformation speed is too fast to generate a large internal stress, which causes the workpiece to be deformed or even cracked. When the water temperature rises, the water contains more gas or water mixed with insoluble impurities (such as oil, soap, mud, etc.), which will significantly reduce its cooling capacity.
The water medium has a low cooling rate in the unstable region of austenite, so that quenching is not hard. Quenched parts also generate tremendous stress during quenching, causing cracking and deformation. The vapor film stage is long and bubbles are easily generated. The steam in the grooves and holes of the quenching member is not easily escaped, resulting in uneven cooling, so that quenching soft spots are prone to occur.
As the temperature increases, the temperature characteristic temperature of the water medium decreases, and the cooling rate of the workpiece at the same cooling temperature decreases. The water medium has been shown to be slower and faster in the three cooling stages, and the cooling rate characteristics are exactly opposite to the ideal one. Therefore, it is easy to cause quenching deformation and cracking.
When the water temperature is lower than 10 °C, large thermal stress will occur, resulting in increased deformation of the quenching part; when the water temperature exceeds 30 °C, the workpiece is difficult to harden. Therefore, the tap water for quenching and cooling is often controlled within the range of 15 to 30 °C.
In order to increase the critical cooling rate, shorten the vapor film time, and improve the cooling uniformity, it is generally possible to use the up and down shaking operation to make the water circulation to reduce the stability of the vapor film.
The characteristic temperature of distilled water was 350 °C. The cooling rate at 400 ° C is less than that of static tap water, which is 150 ° C / s. At 200 ° C, the cooling rate is close to the static tap water. Therefore, the cooling water is worse than the tap water, and the cost is high, so distilled water is generally not used as the quenching agent.
[Main use] It is suitable for quenching of carbon steel parts with small cross-section and shape, and the working surface is smooth.
[Precautions for use]
1 It is best to use stirring or forced circulation to improve the uniformity of cooling and prevent soft spots and deformation.
2 Do not mix impurities such as dust and oil in the water.
3 Working temperature should be ≤ 40 °C.
002 tap water medium
[Introduction] Tap water is the cheapest common quenching agent in nature. The utility model has the advantages of high vaporization heat, high heat transfer coefficient, convenient use, low price, stable composition and no deterioration. However, the cooling rate changes significantly with changes in water temperature. The working temperature of the medium should not be as much as 40 °C.
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] The quenching and cooling characteristics can be referred to as "stationary water medium". Tap water has a low cooling rate in unstable regions of austenite, so quenching is not hard. Quenched parts also generate tremendous stress during quenching, causing cracking and deformation. The vapor film stage is long and bubbles are easily generated. The steam does not easily escape in the grooves and holes of the quenching member, resulting in uneven cooling, and thus soft spots are liable to occur.
The results of the 20mm standard silver ball experiment show that the characteristic temperature of the tap water is 400 ° C at 20 ° C. At this temperature. The average cooling rate of the medium is about 200 ° C / s. The workpiece temperature is in the vapor film stage above 400 ° C and lasts for a long time. Therefore, the vapor film inside the groove of the quenched workpiece is very stable and difficult to be broken, so that the Ling is uneven, and the surface is prone to soft spots; when the surface temperature of the workpiece is below 400 ° C, the boiling speed is sharply increased. The cooling rate is about 700 ° C / s at 200 ° C. The maximum value reached 775 ° C / s at 340 ° C.
There is no cooling performance index of tap water in ISO9950 standard, and the cooling performance of tap water at 30 °C is shown in Table 2-1. The temperature at which the maximum cooling rate is located differs greatly in different literatures, between approximately 530 and 630 °C. But mainly at around 550 °C ± 20 °C.
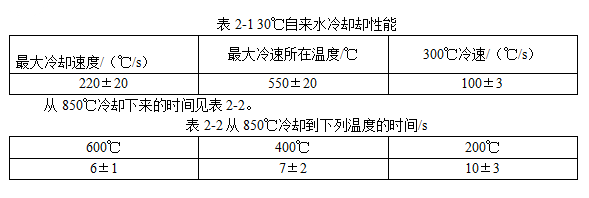
[Main use] Tap water is generally only used for quenching of carbon steel parts with small cross sections and simple shapes.
[Precautions for use]
1 It is best to use stirring or forced circulation to improve the uniformity of cooling and prevent soft spots and deformation.
2 Do not mix impurities such as dust and oil in the water.
003 boiling water medium
[Introduction] The boiling water quenching at 100 °C is called HOWAQ method. When the workpiece is put into boiling water, the surface does not pass through the vapor film stage and directly enters the boiling cooling stage. The boiling water quenching does not require temperature adjustment, but it ensures stable cooling conditions. A better hardening effect can be obtained.
ã€The main purpose】
1 can be used for quenching hardening, and the uniform normalizing of low carbon steel below 35 steel can improve the deep drawing performance of mild steel.
2 can be used for the collapse of the complex workpiece with grooves after heating in the salt furnace.
004 sodium chloride aqueous solution
[Introduction] Sodium chloride (salt) can adhere to the surface of hot quenching parts, violently exploding into a mist (cracking), causing the vapor film to break, and the vapor film stage is greatly shortened, thereby significantly increasing the cooling rate of water and cooling. Also more uniform. The price is cheap, the quenching part can reach higher hardness and the hardness is even. The composition is stable and easy to use.
The disadvantage of this medium is that the cooling rate varies with the temperature of the solution, and the quenched parts are apt to rust after quenching. The concentration of the aqueous solution of NaCl (mass fraction) can be 5% or 10%.
[Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] The vapor film phase of the saline solution is short. At normal temperature, when the concentration (mass fraction) is <15%, the cooling capacity increases with the increase of concentration; when the concentration (mass fraction) is >20%, the cooling capacity decreases with the increase of concentration.
The concentration of the saline solution starts from 5%, and the vapor film stage almost disappears. The vapor film of the solution with a concentration of 15% has the fastest crack. At 20 ° C, the characteristic temperature of the 10% saline solution medium was 650 °C. The cooling rate was 2200 ° C / s at 400 ° C. The cooling rate at 200 ° C is 700 ° C / s. Generally, a 5% to 15% aqueous salt solution is used as a quenching agent.
Compared with pure water, 5% to 15% of saline solution has a strong cooling ability in a high temperature zone. The actual hardened layer of steel is increased. The cooling uniformity is higher. This prevents the appearance of soft spots. However, it will cause a large thermal stress; in the temperature range of 300 to 200 ° C, its cooling rate is faster than pure water. At <200 ° C, it is equivalent to pure water. This will reduce tissue stress.
The cooling capacity of the brine solution is greatly affected by the temperature. Raise the liquid temperature to reduce the heat of vaporization of the solution. The cooling rate is increased by adjusting the vapor film time. When the temperature of the 10% saline solution is increased, the cooling rate in the middle temperature zone can be lowered. There is little change in the cooling rate in the low temperature zone below 250 °C, which reduces the cooling uniformity. Therefore, the salt solution temperature is generally controlled to <40 ° C.
25% to 30% of the saturated experimental aqueous solution has a large viscosity, which will reduce the cooling rate in the high temperature zone or the low temperature zone. Therefore, it is possible to obtain better prevention of deformation and cracking effects in the case where the quenching hardness is slightly lowered.
ã€The main purpose】
1 For quenching parts with low hardenability, not easy to crack, and low requirements for preventing deformation, such as carbon steel (effective thickness 30-100mm, using salt water, oil quenching), alloy structural steel (40Cr, 40CrrMoV, effective thickness 30 ~150mm; 38CrMoAl effective thickness >80mm.).
2 In view of the high cooling strength of 5% to 15% saline solution medium, it can be used for single-liquid quenching of carbon structural steel workpieces and rapid cooling medium for carbon tool two-liquid quenching.
3 In production, 25% to 30% of saturated brine can be used as quenching medium for high carbon steel and some microalloyed steel parts.
[Precautions for use] The temperature of the solution should be controlled at <60 °C during use. It should be cleaned in time after quenching and rust-proofed.
005 saturated calcium chloride aqueous solution
[Introduction] It has quenching and cooling characteristics similar to that of saline solution. However, calcium chloride costs are higher. A dilute aqueous solution of calcium chloride is generally not used as a quenching agent. The disadvantage is that when the temperature is too low, calcium chloride crystals will precipitate and block the quenching tank line. Quenching parts are prone to rust when placed.
After quenching with saturated calcium chloride, the surface is silver-gray, but the residual salt adhering to the surface of the workpiece and the continuous working conveying member should be cleaned up in time. At present, it is correspondingly used for mass production, and there are still some difficulties due to the unsolved rust prevention problem.
In the austenite unstable zone (650 ~ 550 ° C), there is a high cooling rate, in the martensite transformation zone, because its boiling point is higher than water, the convection starting temperature is also higher, and its viscosity ratio The water is large and the heat transfer is also poor. Therefore, the cooling rate is slow, thereby reducing the quenching stress and preventing deformation and cracking.
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] The cooling curve of the quenching agent conforms to the ideal cooling curve, and the cooling capacity is between water and oil cooling. When the hot workpiece enters a saturated calcium chloride solution with a density of Ρ=1.40g/cm^3 (the composition is: anhydrous calcium chloride 48, water 52%), the cooling rate in the vapor film stage is larger, the maximum cold The rate is 230 ° C / s at 670 ° C. In the low temperature stage where the microstructure of the steel undergoes martensite transformation, the cooling rate is the smallest. The average cooling rate in the temperature range of 300 to 200 ° C is 49 ° C / s.
When the temperature of the saturated calcium chloride aqueous solution is too low, more crystals are precipitated; when the temperature is too high, the medium will boil and the cooling performance is deteriorated. Therefore, the temperature of the calcium chloride quenching agent is generally controlled between 10 and 70 ° C in production.
[Quenching agent composition]
1 The cooling capacity is controlled according to the density of the measured medium during production. The medium of the saturated calcium chloride aqueous solution is usually selected from 1.36 to 1.42 g/cm 3 and from 1.44 to 1.48 g/cm 3 .
2 When preparing calcium chloride aqueous solution, anhydrous powder or crystal should be added to tap water in batches. Heating is also required if necessary to promote rapid dissolution of calcium chloride.
The concentration of the aqueous solution of calcium chloride cannot be too high. When the density Ï>1.48g/cm^3, the crystal is easily precipitated. When the temperature of the medium is too low, the solution with a lower density will precipitate crystals.
ã€The main purpose】
1 It can be applied to the quenching of carbon steel structural steel, carbon tool steel, ductile iron and some steel workpieces.
2 can be used for water and oil two-liquid quenching.
3 Instead of oil quenching, the medium has a promotional value.
[Precautions for use]
1 After quenching, it is necessary to cool the workpiece to remove it, otherwise the calcium chloride will evaporate to produce a pungent odor.
2 After quenching, quenching parts should be cleaned in time for anti-rust treatment.
3 If the nitrate salt is mixed into the medium, it will react to form ammonia gas, which will adhere to the surface of the workpiece, resulting in soft spots.
4 When the large workpiece or workpiece is in close contact, it must be cooled by reinforced circulation, otherwise the quenching soft point will appear.
006 zinc chloride-calcium chloride aqueous solution
[Introduction] In order to increase the solubility of the aqueous calcium chloride solution at the same temperature, zinc oxide is added to prepare a medium of zinc chloride-calcium chloride aqueous solution.
Due to the high solubility of zinc chloride and calcium chloride, the temperature and concentration of the medium are high.
2 The working temperature should be controlled between 20 and 60 °C.
008 magnesium chloride aqueous solution
[Introduction] When the aqueous solution of magnesium chloride is high concentration, the boiling point and viscosity are high, the cooling rate in the low temperature stage (100-300 °C) is significantly reduced, and the high cooling rate in the high temperature zone (~600 °C) can quench the workpiece. Higher hardness is obtained afterwards and deformation and cracking are reduced.
Adding an appropriate amount of inorganic salt, alkali or a mixture thereof to water to form various inorganic aqueous solutions can improve the cooling rate of the workpiece in a high temperature zone, improve the cooling uniformity, obtain a higher hardness after quenching the workpiece, and reduce quenching cracking. And deformation, non-toxic, non-polluting, easy to clean the workpiece, easy to use and manage.
ã€The main purpose】
1 can be applied to the quenching of carbon structural steel, carbon tool steel, ductile iron and some alloy steel workpieces.
2 can be used for water and oil two-liquid quenching.
009 sodium carbonate aqueous solution
[Introduction] The performance and use of the medium is similar to that of sodium chloride aqueous solution, but its effective thickness for quenching is only l/3. The medium can adhere to the surface of the hot quenching part, violently explodes into a mist (cracking), destroys the vapor film, and the vapor film stage is greatly shortened, thereby increasing the cooling rate of the water.
There are two types of quenching agents.
A low concentration aqueous solution of 13% to 5% (mass fraction) sodium carbonate.
215% to 20% (mass fraction) of a higher concentration aqueous solution of sodium carbonate.
ã€The main purpose】
1 Containing 3% to 5% (mass fraction) sodium carbonate, used for quenching of standard parts of 35 steel machine tools, reducing deformation and preventing cracking. The medium cooling performance is similar to that of the saline solution medium.
2 Some units also use 16% sodium carbonate as the quenching medium for GCr15 bearing steel balls. When used in the temperature range of 20 to 45 °C, it can eliminate the quenching soft point and improve the hardness uniformity without reducing the hardness.
3 Suitable for bearing steel with effective thickness >25mm, the surface of the workpiece is smoother.
[Precautions for use]
1 Avoid heating with salt of cerium chloride. Otherwise, cerium carbonate precipitation will be formed in the medium, and the quenching cooling characteristics will be changed to increase the quenching dispersion.
2 The working temperature of the medium should be ≤60 °C.
010 dinitrogen solution
[Introduction] Supersaturated nitrate aqueous solution has the advantage of being in the high temperature zone (650-550 °C). Due to the presence of a large amount of nitrate, the formation and stability of the vapor film are destroyed, and the cooling rate is close to that of water. In the low temperature zone (300 ~ 200 ° C), due to the high concentration of the Lok solution, the viscosity is large, the fluidity is poor, the convection speed is 幔, and the cooling rate is close to the oil. The aqueous solution of dinitrogen is similar to the saturated calcium chloride solution, has high quenching hardness, deep hardened layer, small deformation and is not easy to crack. Quenching parts have good rust resistance. The quenching cooling characteristics are between water and oil. The cooling rate is 3 times faster than oil at high temperature and 1 times higher than that at low temperature, but still slower than water.
The disadvantage is that the price is much higher than that of calcium chloride. Sodium nitrite is toxic and prone to carcinogens.
Quenching agent formula (mass fraction): The aqueous dinitrogen solution contains 31.2% NaNO3, 20.8% NaNO2, and the balance is water, and the density is 1.44g/cm^3. The relative density used should be controlled between 0.36 and 1.41.
The solution has a cooling rate of 4.26 ° C / s and 0.336 ° C / s with respect to water at 650 to 550 ° C and 300 to 200 ° C.
ã€The main purpose】
1 It is suitable for quenching of T10A punch, T8A tap, 40Cr shaft and ejector rod, and has the advantage of small cracking tendency. However, during use, the quenching agent forms a precipitate at the bottom of the cooling tank earlier, and the nitrate salt on the jig enters the salt bath heating furnace, which increases the oxidizing component of the heating medium.
2 For the quenching of medium carbon copper, high carbon steel, low alloy and spheroidal castings, it can also replace the water-oil two-liquid quenching of carbon steel. 45 steel effective thickness ≤ 40mm.
3 alloy steel with simple shape, such as 40Cr, 6sMn, 20Cr (after carburizing), GCr15 workpiece.
[Precautions for use]
1 Sodium nitrite is toxic and has carcinogenic effects. It should be replaced with non-toxic rust inhibitor.
2 The use temperature is 30 to 60 °C. When the temperature rises to 100 ° C, the cooling capacity will drop and soft spots will appear.
011 trinitrogen solution
[Introduction] The aqueous solution of trinitrogen is a high-concentration supersaturated nitrate aqueous solution. Similar to the saturated calcium oxide solution, the quenching hardness is high, the hardened layer is deep, the deformation is small, and it is not easy to crack. The quenching parts have good rust resistance, and the quenching cooling characteristics are between water and oil. The cooling rate is 3 times faster than the oil medium at high temperature and 1 times that of the oil medium at low temperature, but still slower than water. The price of the medium is much higher than that of calcium chloride, which is toxic and prone to carcinogens.
Quenching agent formula (mass fraction): 25% sodium nitrate, 20% sodium nitrite, 20% potassium nitrate, 35% water.
The density is controlled at: 1.40 to 1.45 g/cm^3 for carbon steel and 1.45 to 1.50 g/cm^3 for low alloy steel.
At high temperatures (500 to 650 ° C), the vapor film is formed due to the precipitation of salt crystals, and the cooling ability is close to that of water. At low temperatures (200 to 300 ° C), the concentration is extremely high, the fluidity is poor, and the cooling capacity is close to that of oil.
ã€The main purpose】
1 can replace water-oil double medium quenching.
2 Used for quenching of medium carbon steel, high carbon steel, low alloy and spheroidal castings.
3 can replace the water-oil two-liquid quenching of carbon steel. 45 steel effective thickness ≤ 40mm.
4 pairs of 40Cr, 65Mn, 20Cr carburized, GCr15 and other alloy steel simple parts can also be used three-nitrate aqueous solution quenching agent.
5 The medium is suitable for ordinary medium and high carbon steel simple parts and ductile iron quenching parts.
6 For carbon structural steel complex parts, quenching with three-nitrogen aqueous solution and oil two-liquid quenching, the deformation cracking tendency is smaller than that of brine and oil two-liquid quenching.
[Precautions for use]
1 The medium can be used in the range of room temperature to 70 ° C, especially 38 ° C. When the temperature of the medium rises to 100 ° C, the cooling capacity will drop and soft spots will appear.
2 The medium quenching tank should be equipped with a steam heating pipe and a cooling water pipe.
3 The use of the quenching agent will bring the nitrate salt to the ground, so care should be taken to prevent the fire.
4 The medium is not used for more than 24 hours. It is best to use air or mechanical stirring when reusing, so as to avoid precipitation of the solution and affect the quenching effect. The nitrate salt adhered to the salt furnace, card and hanger should be removed in time to avoid being brought into the salt furnace. A splash occurred, causing a burn accident.
5 Sodium nitrite has toxicity and carcinogenic effects, and should be replaced with non-toxic rust inhibitor.
012 copper sulfate aqueous solution I
[Introduction] Compared with the saline solution, the medium has a faster cooling rate in the cooled high temperature zone and a slower cooling rate in the low temperature zone. Therefore, the copper sulfate aqueous solution is a good cooling medium. However, the copper sulfate aqueous solution is toxic to the human body, and the precipitation is not easy to remove on the surface of the workpiece. When the workpiece is cooled, as the metal is continuously precipitated, more copper ions are taken out by the workpiece in atomic form, so that the composition of the medium and the cooling performance occur. change. Limit its application.
Quenchant formulation (mass fraction): 250g/LCuSO4·5H2O+75g/LH2SO4, density 1.82g/cm^3.
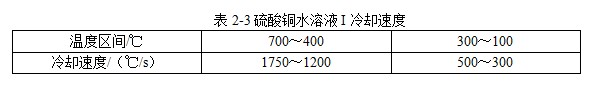
[Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] When a hot workpiece is quenched into a copper sulfate aqueous solution, metallic copper is strongly precipitated on the surface of the workpiece, thereby destroying the formation of the vapor film, shortening the duration of the vapor film, and increasing the cooling rate in the high temperature region. At the same time, due to the influence of convection stage and sedimentation, the cooling rate in the low temperature zone is also smaller, which is in line with the ideal cooling curve (Table 2-3).
013 copper sulfate aqueous solution II
[Quenching agent formula] Reference formula (mass fraction): 30g / L CuSO4 · 5H2O + 100mg NH4OH (25%) + 120g / L H2C2O4 (oxalic acid) + 35g / L NaF + H2PO4.
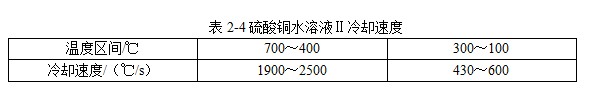
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] The same as 012 aqueous copper sulfate solution I, see Table 2-4.
014 water glass (sodium silicate) aqueous solution
[Introduction] The medium is inexpensive and is often used to replace the water quenching oil cold medium. Such media include "114" quenching media, "413" emulsions, and the like.
Quenching agent composition: single water glass solution, modulus M = SiO2 / Na2O = 2.4, relative density of 1.09l ~ 1.125 (12 ~ 16 wave US dollars) (sodium silicate can be replaced by potassium silicate).
[Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] The cooling of the aqueous solution of water glass can be controlled by changing the content of sodium silicate (potassium) and the temperature of the solution. The larger the modulus of water glass [the modulus M of water glass is expressed by the ratio of the moles of silicon oxide to sodium oxide (or potassium)], the higher the silicon oxide content in the medium, the greater the concentration of the medium, and the other conditions. At the same time, the cooling capacity of the aqueous solution of water glass increases as the modulus decreases. Increasing the temperature of the medium slows down its cooling rate.
The cooling curve of the aqueous solution containing water with a single water glass and water does not change in principle. However, by adding a certain amount of sodium hydroxide to different concentrations of water glass, the medium can be brought close to the cooling performance of the oil.
ã€The main purpose】
1 sodium silicate solution can be used as a spring steel 65Mn, 60Si2Mn and other automotive and tractor spring plate quenching cooling medium to replace mechanical oil and spindle oil without reducing the mechanical properties of the product.
The automobile leaf spring of 260Si2Mn steel is quenched at 840 ° C, then tempered at 460 ° C, and the working temperature of the medium is 60-70 ° C. The leaf spring treated with a 16-wave solution can increase the fatigue life by 6.7 to 10 times (up to 4 million times) than oil quenching (400,000 times).
3 Quenched in a sodium silicate water glass solution with a modulus M=2.4 and a Baume concentration of 15°Bé, and a 60Si2Mn leaf spring tempered at 460°C. The metallographic structure is the same as the oil quenching, and both are tempered troostite. + tempered sorbite + a small amount of massive ferrite. The mechanical properties of the leaf spring and the fatigue life of the spring assembly have an increasing trend.
[Precautions for use]
1 If the quenching is performed at a liquid temperature of <50 ° C, the workpiece is prone to quenching cracks. When the liquid temperature is too high, boiling will occur, and it is difficult to obtain a high quenching hardness. Moreover, it is necessary to move up and down in time while the workpiece is being cooled, otherwise there will be no quenching or uneven hardness. Therefore, the use temperature is best at 60 to 70 °C.
2 The water glass component of the quenching agent is stable. However, if the water volatilizes more, density measurement is often performed to provide a basis for adjusting the moisture.
3 After the quenching, the white deposit on the surface of the workpiece will not cause corrosion.
015 "114" quenching agent
[Quenching agent composition] In a water glass aqueous solution having a density of 1.10 to 1.12 g/cm 3 , NaOH is added to adjust the relative density to 1.14, which has the advantage of reducing deformation and avoiding cracking.
[Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] The medium has a cooling capacity between water and oil. In the low temperature zone (300 ~ 200 ° C), water glass can form a layer of ductile film around the workpiece, so the cooling rate is significantly reduced. Its cooling rate is adjustable.
ã€The main purpose】
1 Used for quenching of 60Si2Mn steel automotive leaf springs.
2 For the quenching of carbon steel workpieces with complex shapes and uneven thickness.
3 is used for quenching of bearing steel and the like.
4 For large quantities of oil quenched workpieces, can be used as a substitute for oil.
[Precautions for use]
1 The water glass component of the quenching agent is stable, but the water volatilizes more, so the density measurement is often performed to provide a basis for adjusting the moisture.
2 The surface of the workpiece will adhere to the colloidal sodium silicate, which is difficult to clean. It has a corrosive effect on the surface of the workpiece.
016 "413" emulsion quenching agent
[Quenching agent composition and preparation]
1 Reference formula (mass fraction): Na2SiO3 66%, NaOH 8%, and the rest is groundwater.
2 Preparation method: firstly mix the water into the water glass to obtain a solution with a density of 1.27~1.30g/cm^3, and then add the industrial caustic soda with a total weight of the mixture of 7%-10%, and the density after stirring evenly It is 1.32 to 1.36 g/cm^3. All preparation processes are monitored based on the density of the solution.
3 The chemical composition of the newly prepared solution: 19% to 20% of SiO2, 10.5% to 12.5% ​​of Na2O, and 3.2% to 5.5% of Na2SiO3.
[Quenching and Cooling Characteristics] When a hot workpiece is immersed in the emulsion, a layer of sodium silicate film is formed on the surface of the workpiece, and the first stage cooling is slowed down, followed by surface film bursting. The workpiece begins to cool directly in the emulsion medium, and the cooling rate is large; when the explosion process stops, the film re-forms and the third stage cools down. Thus, cracking and deformation of the workpiece can be effectively reduced.
The quenching medium is easy to prepare and operate, does not catch fire, is safe to use, improves working conditions, and can save a lot of oil. The use temperature is 30 to 50 °C.
ã€The main purpose】
1 The medium can be used for quenching and tempering of high carbon tool steel, low carbon structural steel, 40Cr, 40MnB, 9CrSi and cast steel ZG40MnB, etc., instead of quenching oil, to ensure that the mechanical properties are not reduced.
2 The medium has difficulty in processing mold steels such as GCr15, 5CrMnMo, 5CrNiMo, 3Cr2W8VA and 3Cr3.
017 No. 8 quenching agent
[Introduction] No. 3 quenching agent is an aqueous solution of alkali nitrate. The quality of the boat is compared with water. The cooling rate is smaller in the high temperature range and smaller in the low temperature range. The use temperature is between 20 and 60 °C.
Quenching agent formula (mass fraction): NaOH 49%, NaNO3 25%, KNO3 26%, H2O 35%.
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] At 630 ° C, the No. 3 quenching agent has the highest cooling rate, and the value is 406 ° C / s. In the high temperature region of 650 to 550 ° C, the cooling rate is 375 ° C / s; in the low temperature region of 300 to 200 ° C, the cooling rate is 77 ° C / s.
[Main use] It can be used for quenching steels such as 45, 40Cr, 9SiCr, 65Mn, GCr15, 20Cr, and 18CrMnTi with simple shapes.
018 "351" with water substitute oil quenching agent
[Introduction] This medium is useful to prevent the solution from undergoing chemical changes. The cooling capacity of the main component of water glass is between water and oil. In the low temperature range of 300 to 200 ° C, water glass can form a layer of ductile film around the workpiece, so the cooling rate is significantly reduced. It has an adjustable cooling rate and can be used as a quenching oil substitute. The medium has a boiling point of 108 °C.
When the medium is used, colloidal sodium silicate adheres to the surface of the workpiece, which is difficult to clean and has a corrosive effect on the surface of the workpiece.
[Medium composition] Quenching agent formula (mass fraction): sodium chloride (salt salt) 11% ~ 13%, sodium carbonate 11% ~ 13%, water glass (Bome degree 56 ° Bé) 20% ~ 26%, the remainder water.
According to the above mass fraction, sodium carbonate is first sprinkled into water, and after dissolution, sodium chloride is added. After the sodium chloride is completely dissolved, the concentration of the solution is 25 to 28 ° Bé, and the water glass is added to make the solution into a slag-free translucent emulsion (Pomez is 30 to 34 ° Bé). . The emulsion is heated to a high temperature, and then cooled to room temperature, and repeated several times until the solute is sufficiently dissolved.
[Quenching and cooling characteristics] Compared with No. 20 oil, the "351" quenching agent is in the range of 650-450 °C. The former has a slower cooling rate than oil, but it greatly exceeds the critical cooling rate of low-alloy steel. Below the Ms point The cooling rate is faster than oil. By adjusting the amplitude and frequency of the workpiece turbulence, or the speed of movement, the cooling characteristics of the "351" quenching agent can be made comparable to that of No. 20 oil.
ã€The main purpose】
1 Used for quenching of 60Si2Mn steel automotive leaf springs.
2 For the quenching of carbon steel workpieces with complex shapes and uneven thickness.
3 is used for quenching of bearing steel and the like.
4 for large-volume oil quenched workpieces, can be used as a substitute for oil
[Precautions for use]
1 The workpiece is heated by a 50% salt bath of sodium chloride and sodium carbonate. The loss of sodium chloride and sodium carbonate in the medium will be “naturally†supplemented. The total content of the two components can be maintained at about 26%. Yes, the water and water glass content should be replenished regularly or at any time.
If the workpiece is heated by a salt bath containing barium chloride, the barium chloride brought into the medium from the salt bath reacts with sodium carbonate to form a precipitate of barium carbonate, which increases the loss of sodium carbonate. At this time, it is necessary to find an additive by the test. The amount of sodium carbonate.
With other heating equipment, the lost "351" quenching agent should be added according to the original formula.
2 The quenching agent can be used at 20 to 80 ° C, and the optimum use temperature is 30 to 65 ° C.
019 water glass · oxide aqueous solution
[Introduction] The former Soviet Union patent quenching medium. Cooling quenching in the quenching agent ensures hardness, no harmful precipitates, and stable rust resistance on the surface of the part.
Quenching agent formula (mass fraction): water glass 18% to 20% (volume percent), silica 32% to 34%, sodium oxide 12.5% ​​to 13.5%, and the balance is water.
ã€The main purpose】
1 can be used for the quenching of carbon steel workpieces with complex shapes and uneven thickness.
2 is used for quenching of bearing steel and the like.
020 caustic soda and sodium salt quenching agent
[Introduction] The surface of the quenched parts in this medium is smooth and free of quenching cracks. The quenching quality is guaranteed for mass production and can be used instead of oil quenching.
Quenching formula (mass fraction): 3% to 5% NaOH, 6% to 8% Na2CO3, 15% to 20% Na2SiO3, and the balance is water.
After preparation, the density of the medium is 1.5 ~ 1.75g ​​/ cm3. I am water. The use temperature is 30 to 60 °C.
[Main use] The medium is quenched on the GCr15 steel surface grinder bushing, the hardness is uniform, and the hardness is as high as 64-66HRC.
Measuring Tape,Metric Tape Measure,Rolling Tape Measure,Metric Tape
SHANGQIU CHAOYUE MEASURING TOOLS CO., LTD , https://www.equipmentool.com