Preparation process of pre-spinning colored microfiber
Preparation Process of Pre-spinning Colored Microfibers Xing Hao (School of Textile, Tianjin Polytechnic University, Tianjin 300387, China)
Abstract: This paper introduces a method for producing ultra-fine fibers by pre-spinning coloring, which is processed into colored composite microfibers with uniform coloration, high color fastness, super absorbent and decontamination ability, super softness and super-simulation. The corresponding pre-oriented yarn (POY), tensile deformation yarn (DTY), fiber opening process and process parameters are summarized. It is considered that the product eliminates the printing and dyeing process and meets the requirements of energy saving and emission reduction.
Key words: pre-spinning coloration; microfiber; process CLC number: TQ342.21 Document code: BArticle ID: 1001-7054(2012)04-0034-02
As a high-quality textile raw material, microfiber [1] is a typical representative of the development of new synthetic fiber to high technology and high simulation. Its use can effectively improve the grade and added value of the product. The colored composite microfiber product not only has the unique soft hand feeling, moisture wicking, waterproof and breathable, clean and decontamination performance of microfiber, but also meets the textile color requirement, and is a high value-added differential fiber. It is used in high-end fashion fabrics, high-performance wipes, imitation peach skin fabrics, suede materials, gas filter materials and other fields where high dyeing uniformity and fastness are required. It is currently in short supply and has broad prospects. material. However, microfibers also encounter many problems in the dyeing and finishing process. For example, using traditional dyeing and finishing processes, problems such as poor dyeing, poor color fastness, poor uniformity, and poor color control are often encountered. In order to reduce the impact of these problems, this will inevitably increase the production cost, and the impact on the environment is also very serious [2].
The traditional textile process is “spinning and dyeing firstâ€, that is, the fiber is first spun and woven, dyed into various colors by the dyeing factory or printing and dyeing factory, and finally processed into textiles and garments, in which the printing and dyeing stages are required. A large amount of energy consumption and the use of chemical raw materials have become the most serious link in the textile industry chain. Printing and dyeing wastewater not only has a large amount of water, but also has complex composition, deep color, high alkalinity and large organic pollutant content (COD value), which is an intractable industrial wastewater. Therefore, the clean and energy-saving production technology of printing and dyeing industry has always been the focus of researchers at home and abroad. Question. Therefore, if the traditional fiber coloring method can be changed, the pre-spinning coloring technology is used to impart color in the fiber production stage, the printing and dyeing process is omitted, and the direct spinning and weaving is processed into a finished product, which not only saves energy but also enables waste water. zero emission". The textiles produced by the pre-spinning coloring technology satisfy the product's demand for color, and the product has high color fastness, and does not cause dyeing defects such as chromatic aberration, color spots and color flowers. It can be seen that the development and use of fiber pre-spinning technology is of great significance to the environmental protection and sustainable development of the textile industry today, where environmental requirements are becoming higher and the world's water resources problems are becoming more prominent.
This experiment mainly discusses the use of pre-spinning coloring technology and composite spinning technology [3], spinning into a uniform coloring, high color fastness, super absorbent water decontamination ability, super softness and super-simulation color composite superfine fiber.
1. Main raw materials and production equipment Masterbatch, 1.5 mm × 2.5 mm, produced by Goldcolor. Polyester (PET) slice, 4 mm × 2.5 mm, produced by Yizheng Chemical Fiber. Polyamide 6 (PA6) slice, YH800/HYA26, produced by Baling Petrochemical.
PET drying tower, RSFBM-600, Rongsheng Machinery Co., Ltd. PET screw extruder, pa6SJ65, Zhangjiagang Second Light Machinery Co., Ltd. PA6 drying tower, RSF PA6-600, Rongsheng Machinery Co., Ltd. PA6 screw extruder, Φ1204338, Zhangjiagang Second Light Machinery Co., Ltd. Spinneret, Hills. Winder, Barmag.
2. Pre-Oriented Filament (POY) Production Process After the fiber is dried by the masterbatch, it is mixed with the pre-crystallized, dried PET slice and PA6 slice at the screw zone injection port. Before the two-component melt enters the orifice, there are separate channels for extrusion melting, filtration, metering and distribution, and compounding at the moment of entering the orifice. The composite melt enters the spinning hole together, and after cooling out, oiling and winding forming, the process flow is shown in Fig. 1. 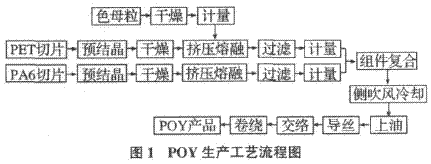
2.1 Main process conditions The mass fraction of the masterbatch is 2% to 3%, the mass fraction of the PET slice is 68% to 72%, and the mass fraction of the PA6 slice is 25% to 30%. The color masterbatch has a drying temperature of 125-135 ° C, a drying time of 5 h, and a moisture content after drying < 2×10-5. The drying temperature of the PET slice was 140 ° C, the drying time was 8 h, and the moisture content after drying was < 2×10-5. The drying temperature of PA6 slice is 120 °C, the drying time is 4~5 h, and the moisture content after drying is <2×10-5.
The temperature of each heating zone of the screw extruder is shown in Table 1. 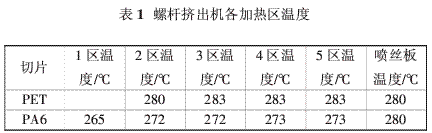
The composite spinning temperature was 280 ° C and the spinning speed was 3000 m / min. The side air supply volume is 32 000 m3/h, the wind pressure is (500±10) Pa, the dry bulb temperature is (20±0.5) °C, the wind speed is 0.4~0.6 m/s, and the relative humidity is 65%~75%. The air temperature is 33~38 °C.
The winding speed is 2800~3000 m/min.
3. Tensile textured yarn (DTY) production process 3.1 Process flow (Figure 2) 
3.2 Main process parameters Heating and stretching: the temperature is 180 ~ 190 ° C, the heating zone is 2 m long, and the stretching ratio is about 1.5.
False æ»: The speed ratio is 1.8.
Shape: temperature 165 ° C, the shape of the length of 1.5 m, the speed of 600 m / min.
Overfeed: The overfeed rate is 3.5%.
Winding: speed 600 m/min.
4.·Opening process 4.1 Process flow The colored composite microfiber produced by this project belongs to split-type superfine fiber. Before the fiber-opening process, there is no obvious difference between the fibril and the conventional fiber. After the fiber-opening process, the composite fiber It is peeled off into ultrafine fibers to reflect the properties of microfibers. The process of opening the fiber is shown in Figure 3. 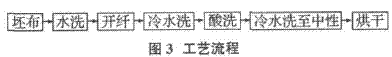
4 .2 Main process conditions Washing: The 2A procedure in GB/T 8629-2001 standard is adopted.
Opening: Bath ratio 1:30, NaOH mass concentration 5 g/L, temperature 110 ° C, time 45 min.
Pickling: The acetic acid solution has a mass concentration of 1 g/L.
Drying: temperature 105 ° C, time 30 min.
5. Conclusion The innovation of this technology is to add the masterbatch to the sliced ​​raw material to meet the pre-spinning requirements of the fiber; the textile produced by the colored composite microfiber does not need to be dyed after weaving, meets the color requirement of the product, and has excellent color fastness. The color fastness of ordinary dyed textiles is uniform, and there are no dyeing defects such as chromatic aberration, color spots and color flowers. It saves the printing and dyeing process, not only saves dyeing materials and energy, shortens the textile industry chain, and truly realizes “zero discharge†of printing and dyeing wastewater. At the same time, the coloring agent used in masterbatch does not contain prohibited structures and components, and does not cause harm to the human body. It is the textile industry. The clean production technology is conducive to environmental protection and is in line with the current industrial policy of energy conservation and emission reduction.
references
[1] Liu Yanyan, Gao Chrom, Han Yan, et al. Determination of the opening ratio of polyester/nickel composite microfibers [J]. Synthetic Fibers, 2006, 35(6): 4-7.
[2]Liu Yuli, Yu Hong. Dyeing characteristics and improvement of polyester microfibers [J]. Guangxi Textile Science and Technology, 2000, 02.
[3]Huang Youpei. Production technology of polyester/jin composite island fiber [J]. Synthetic fiber, 2001, 30 (6): 39-40.
Animal Feed Additive,Microbial Organic Agent,Seaweed Biobacterial Agent
Well Chemical Co., Limited , http://www.chemistryr.com