Research progress on photothermal co-catalysis at Dalian Institute of Chemical Technology
Recently, the Dalian Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Catalysis and New Materials Research Center researcher Liu Xiaoyan, Chinese Academy of Sciences Zhang Tao team in light and heat co-catalysis research progress, found that the use of Pt / TiO 2 -WO 3 catalytic oxidation of propane, at low temperatures and high concentrations Under oxygen conditions, the activity of photothermal co-catalysis is much higher than that of photocatalysis and thermocatalysis alone.
Oxidation reactions that use oxygen as an oxidant (such as the elimination of volatile organic pollutants, alkane combustion, etc.) are a very important type of reaction in industrial catalysis, and supported Pt catalysts are one of the highly active catalysts for this type of reaction. However, due to the strong adsorption of oxygen on the surface of Pt, especially in the case of low temperature or high concentration of oxygen, Pt is easily "poisoned" by oxygen and inactivated. Therefore, in traditional thermal catalysis, the activation temperature of such reactions is generally above 200 ℃. The activation of oxygen at high temperature also accelerates the oxidation of metallic Pt, resulting in a decrease in the activity of the supported Pt catalyst.
In view of this, the team used the sub-nanometer Pt supported on the composite semiconductor TiO 2 -WO 3 as a catalyst and propane oxidation as a probe reaction to introduce light on the basis of thermal catalysis to achieve photothermal co-catalysis. The results show that photo-thermal co-catalysis can greatly improve the catalytic oxidation activity of Pt / TiO 2 -WO 3 catalysts for propane under low temperature and high concentration of oxygen. The activity of the catalyst increases with increasing light intensity (0 to 1000 mW / cm2), and T70 (the reaction temperature at which propane is converted to 70%) can be as low as 90 ℃. Compared with thermal catalysis, the maximum temperature difference of T70 can reach 234 ℃. The kinetic study found that the activation energy (Ea) of the photothermal cooperative catalytic reaction decreased linearly with the increase of light intensity, and it could be more than ten times at most. At the same time, the reaction order (n) of oxygen also changes greatly before and after adding light: the reaction order of oxygen is -1.4 when no light is added, and the reaction order of oxygen becomes 0.1 after adding light. This shows that under the photothermal synergistic catalytic conditions, the catalytic activity is almost independent of the oxygen concentration. This work not only solved the problem of oxygen poisoning of the supported Pt catalyst under low temperature and high concentration of oxygen through photo-thermal co-catalysis, but also helped to understand the photo-thermal co-catalysis mechanism of semiconductor-supported non-plasmon metal catalyst.
Relevant research results were published in "German Applied Chemistry" (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.). The above work was supported by the National Key R & D Project, the National Natural Science Foundation Project, the Strategic Leading Science and Technology Special Category B "Essence and Regulation of Energy Chemical Conversion" of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Innovative Group Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Postdoctoral Science Fund Project, and was supported by Shanghai Light .
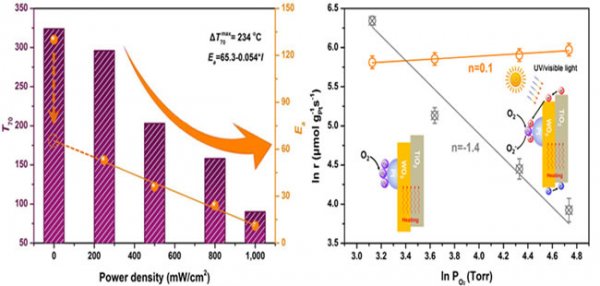
Pt / TiO2-WO3 catalyst under different light intensities T70 and Ea and the change of O2 reaction order with or without light
5M Measuring Tape,Automatic Tape Measure,Tape Measure Scale,Measuring Tape 5 Meter
SHANGQIU CHAOYUE MEASURING TOOLS CO., LTD , https://www.calibrateds.com