Recent situation and application of vacuum carburizing and carbonitriding technology
〠Abstract 】 On the basis of a brief introduction of vacuum carburizing and carbonitriding, the effects and applications of acetylene vacuum carburizing and acetylene and ammonia vacuum carbonitriding are introduced.毫米至0. 08毫米。 After the carburizing layer depth uniformity of the WZST series of double-chamber vacuum carburizing quenching furnace is ±0. 05 ~ 0. 08 mm. When the carburizing depth is from 0.97 to 1.08 mm, the surface carbon concentration is from 0.84 % to 0.88%. After the vacuum-carbonitriding of the 20Cr Mo steel precision gear, the hardened layer has a depth of 0.15 to 0.30 mm and a hardness of 550 HV0. 5 , the diameter of the gear bore is ≤0.11 mm, and there is no bell mouth.
First, the status of vacuum carburizing
1. Propane as a feature of carburizing gas
Bingbing is rich in “C†source, and early vacuum carburizing has always used propane (C3 H8) as carburizing gas. Its characteristics are as follows:
(1) The percolation rate is fast, and high-temperature rapid carburization can be implemented.
(2) There is no grain boundary oxide layer in the layered structure.
(3) It is possible to make complex shapes and carburization without through holes.
2. Propane as a problem of carburizing gas
(1) The amount of installed furnace increases, the flow rate of carburizing gas increases, the pressure increases, and the carbon black is more serious.
(2) Due to the serious carbon black, the frequency of maintenance is accelerated.
(3) In order to reduce the amount of maintenance and frequency, it is necessary to reduce the amount of furnace loading, resulting in low productivity. For this reason, vacuum carburizing stays in the application of special fields and special parts, and it is difficult to promote and popularize.
3. Characteristics of acetylene as carburizing gas
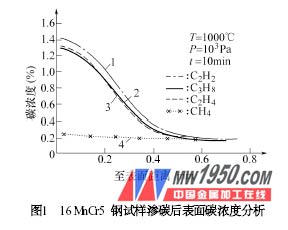
A sample of 16 MnCr5 steel was used for carburizing at 1000 °C and 1 × 103 Pa for 10 min, and then rapidly cooled by 2 × 105 Pa of nitrogen. Four different carburizing gases are used: methane, propane, ethylene and acetylene. The distribution curve of carbon concentration after carburizing of various hydrocarbon gases with MnCr5 steel is shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the carbon concentration on the surface of methane is at least 0.2%, and there is basically no carburizing ability; the carbon concentration on the surface of acetylene is up to 1.4%, and the carburizing ability is the strongest; the results of propane and ethylene are the same. The carburizing capacity is in the middle, and the same carburizing layer is deep, and the carbon concentration is higher by 0.1% when acetylene is used for carburizing. The carbon transport capacity or enrichment rate (g/m2·h) is also the same, methane 2g/ m2 · h, propane and ethylene are 120g / m2 · h and 130g / m2 · h, carbon transport of acetylene The largest, close to 150g / m2 · h.
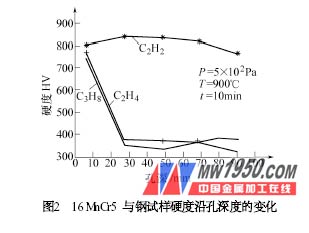
More importantly, different carburizing gases enter the small and deep non-through hole carburizing effect during vacuum carburizing. Test for 3 mm × 90 mm non-through holes, carburize at 900 °C, 5 × 10 2Pa, 10 mi n, rapidly cool in 2 × 105 Pa nitrogen, reheat to 860 °C and quench in 5 × 10 5 Pa nitrogen. Figure 2 shows the results of the test after carburizing with different hydrocarbon gases. It can be clearly seen from the results that the carburizing ability of propane and ethylene can only make the carburizing hardened at a depth of 6 mm without a through hole, and is not infiltrated at > 6 mm. Carburizing with acetylene, along the depth of the hole until the bottom of the hole is 90 mm, all of the carbon is infiltrated. It is obvious that acetylene has obvious and stronger carburizing ability than propane or ethylene. The application of acetylene has brought the development of vacuum carburizing technology into a new stage. The production of carbon black in production is significantly reduced, the maintenance cycle is lengthened, the efficiency is improved, and the furnace capacity is gradually increased to 300-700kg/furnace.
4. Saturated value adjustment method
Figure 3 is a diagram showing the vacuum carburizing process and the saturation value adjustment method on the phase diagram. Gas carburization is the control of the carbon potential of a carburizing atmosphere. Vacuum carburizing is a method of controlling the carburized layer by adjusting the carburizing time to reach the solid solution limit of carbon and the diffusion time after stopping the supply of the carburizing gas. This is called the "saturation value adjustment method".
On the basis of the determination of the flow rate and pressure of the carburizing gas, the time parameter is set, and the reproducibility of the production quality can be conveniently ensured by the automatic control method.
Next page
high quality curve Tunnel Segment Bolt for concrete ring

Application:Permanently fix concrete tunnel segment
Material: Carbon steel or stainless steel----Q235, 35#, 45#, 35CrMo, 42CrMo, 40Cr etc.
Specification:Complete range from M16 to M30 diameters without Length limit.
Finishing;plain(oiled),sherardized,hot dip galvanized, white zink plated, yellow zink plated, black, dacromet, geomet or others specified by the customers
high quality curve Tunnel Segment Bolt for concrete ring
Tunnel Segment Bolt,Curved Tunnel Bolt,Tunnel Bolt,Spear Tunnel Bolt
TAICANG ZHONGBO RAILWAY FASTENING CO., LTD. , https://www.railfastener.com